DSC
In DSC, a small amount of material (approximately 5-10 mg) is heated or cooled. The energy required for this process is compared to a blank reference. Phase transitions (such as glass transition, melting, crystallisation) or reactions (such as oxidation, cross-linking) may either consume or release energy, resulting in a difference in heat flow. By plotting the heat flow against temperature, these phase transitions or reactions can be identified. This test method can be utilised for a variety of purposes, including material type identification, determining the composition of waste streams, and assessing crystallinity or crystallisation rate.
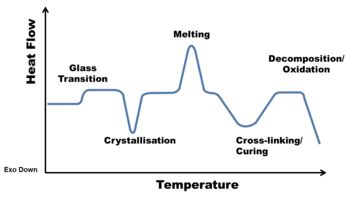
The DSC has a temperature range of -90 °C to 400 °C.
Contact us with any questions and to request your quote.

 Request quotation
Request quotation  Login
Login 
